Compound degraded:Chlordecone
General Description (About POP compound)
Chlordecone (Kepone) is an organochlorine insecticide that has been used as insecticide and fungicide. This pesticide undergoes no significant biotic or abiotic degradation in the environment and is still present in soils where it was applied. It is an obsolete insecticide, related to Mirex and DDT.
Biodegradation pathway
Publications
| Abstract | Title | Authors | Article Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chlordecone (Kepone®) is a synthetic organochlorine insecticide (C10Cl10O) used worldwide mostly during the 1970 and 1980s. Its intensive application in the French West Indies to control the banana black weevil Cosmopolites sordidus led to a massive environmental pollution. Persistence of chlordecone in soils and water for numerous decades even centuries causes global public health and socio-economic concerns. In order to investigate the biodegradability of chlordecone, microbial enrichment cultures from soils contaminated by chlordecone or other organochlorines and from sludge of a wastewater treatment plant have been conducted. Different experimental procedures including original microcosms were carried out anaerobically over long periods of time. GC-MS monitoring resulted in the detection of chlorinated derivatives in several cultures, consistent with chlordecone biotransformation. More interestingly, disappearance of chlordecone (50 ?g/mL) in two bacterial consortia was concomitant with the accumulation of a major metabolite of formula C9Cl5H3 (named B1) as well as two minor metabolites C10Cl9HO (named A1) and C9Cl4H4 (named B3). Finally, we report the isolation and the complete genomic sequences of two new Citrobacter isolates, closely related to Citrobacter amalonaticus, and that were capable of reproducing chlordecone transformation. Further characterization of these Citrobacter strains should yield deeper insights into the mechanisms involved in this transformation process. | Microbial Degradation of a Recalcitrant Pesticide: Chlordecone | Chaussonnerie et al., 2016 | Link |
| Chlordecone (CLD) is a very persistent synthetic organochlorine pesticide found in the French West Indies. Recently published work has demonstrated the potential of zero-valent iron to dechlorinate CLD by in situ chemical reduction (ISCR) in soils under water-saturated conditions, forming mono- to penta-dechlorinated CLD transformation products. These transformation products are more mobile than CLD and less toxic; however, nothing is known about their further degradation, although increasing evidence of CLD biodegradation by bacteria is being found. The present study began with the enrichment from wastewater sludge of a CLD-transforming community which was then inoculated into fresh media in the presence of either CLD or two of the main ISCR transformation products, 10-monohydroCLD (-1Cl-CLD) and tri-hydroCLD (-3Cl-CLD). Carried out in triplicate batches and incubated at 38°C under anoxic conditions and in the dark, the cultures were sampled regularly during 3 months and analyzed for CLD, -1Cl-CLD, -3Cl-CLD, and possible transformation products by gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. All batches showed a decrease in the amended substrates (CLD or hydroCLD). CLD degradation occurred with concomitant formation of a nine-carbon compound (pentachloroindene) and two sulfur-containing transformation products (chlordecthiol, CLD-SH; methyl chlordecsulfide, CLD-SCH3), demonstrating competing transformation pathways. In contrast, -1Cl-CLD and -3Cl-CLD only underwent a sequential reductive sulfidation/S-methylation process resulting in -1Cl-CLD-SH and -1Cl-CLD-SCH3 on the one hand, and -3Cl-CLD-SH, -3Cl-CLD-SCH3 on the other hand. Some sulfur-containing transformation products have been reported previously with single bacterial strains, but never in the presence of a complex microbial community. At the end of the experiment, bacterial and archaeal populations were investigated by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. The observed diversity was mostly similar in the CLD and -1Cl-CLD conditions to the inoculum with a dominant archaea genus, Methanobacterium, and four OTU affiliated to bacteria, identified at the family (Spirochaetaceae) or genus level (Desulfovibrio, Aminobacterium, and Soehngenia). On the other hand, in the -3Cl-CLD condition, although the same OTU were found, Clostridium sensu stricto 7, Candidatus Cloacimonas, and Proteiniphilum were also present at > 2% sequences. Presence of methanogens and sulfate-reducing bacteria could contribute to sulfidation and S-methylation biotransformations. Overall, these results contribute to increasing our knowledge on the biodegradability of CLD and its transformation products, helping to progress toward effective remediation solutions. | Microbial Transformation of Chlordecone and Two Transformation Products Formed During in situ Chemical Reduction | Hellal et al., 2021 | Link |
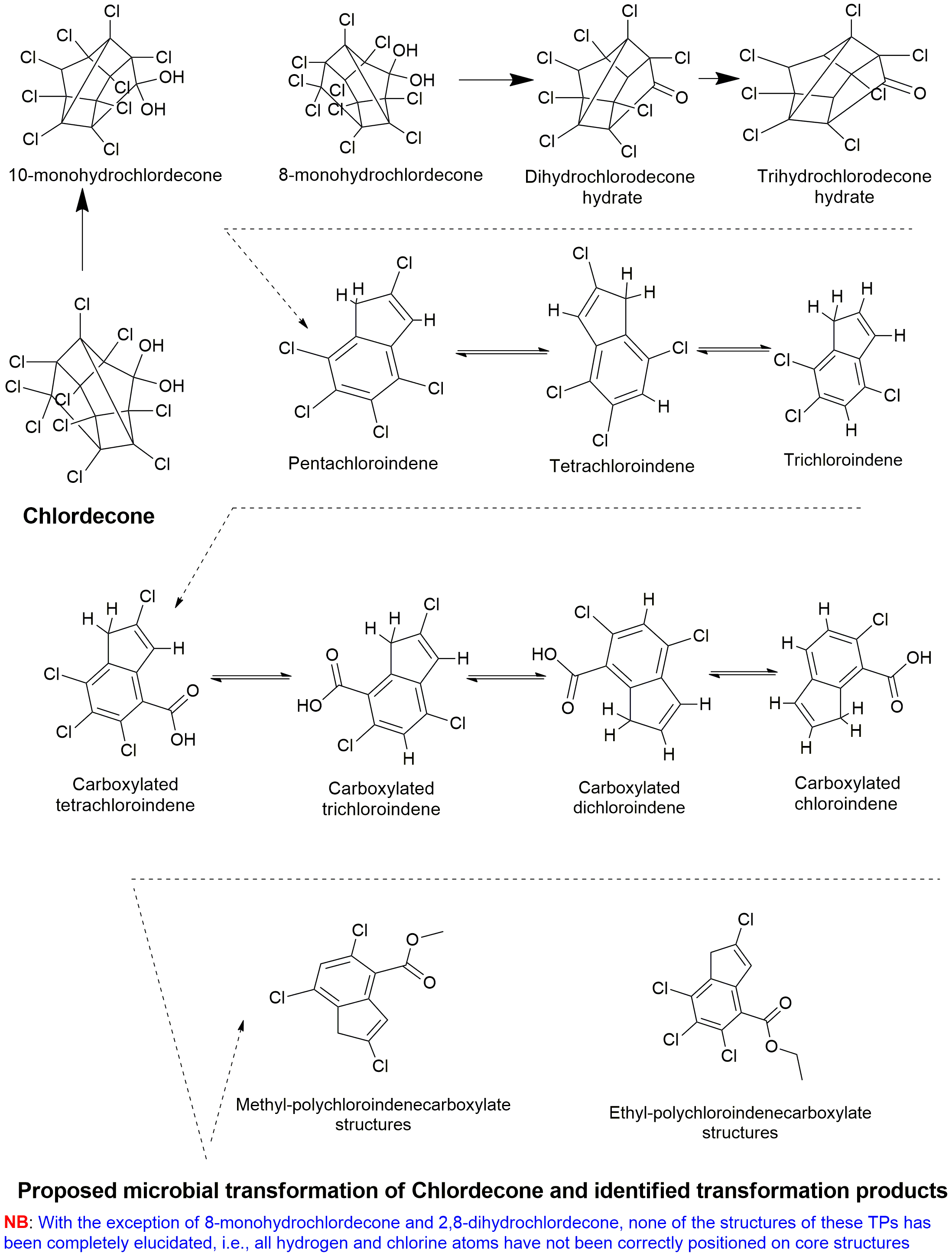
| Production and use of the insecticide chlordecone has caused long-term environmental pollution in the James River area and the French West Indies (FWI) that has resulted in acute human-health problems and a social crisis. High levels of chlordecone in FWI soils, even after its ban decades ago, and the absence of detection of transformation products (TPs), have suggested that chlordecone is virtually nonbiodegradable in the environment. Here, we investigated laboratory biodegradation, consisting of bacterial liquid cultures and microcosms inoculated with FWI soils, using a dual nontargeted GC-MS and LC-HRMS approach. In addition to previously reported, partly characterized hydrochlordecones and polychloroindenes (families A and B), we discovered 14 new chlordecone TPs, assigned to four families (B, C, D, and E). Organic synthesis and NMR analyses allowed us to achieve the complete structural elucidation of 19 TPs. Members of TP families A, B, C, and E were detected in soil, sediment, and water samples from Martinique and include 17 TPs not initially found in commercial chlordecone formulations. 2,4,5,6,7-Pentachloroindene was the most prominent TP, with levels similar to those of chlordecone. Overall, our results clearly show that chlordecone pollution extends beyond the parent chlordecone molecule and includes a considerable number of previously undetected TPs. Structural diversity of the identified TPs illustrates the complexity of chlordecone degradation in the environment and raises the possibility of extensive worldwide pollution of soil and aquatic ecosystems by chlordecone TPs. | Natural Chlordecone Degradation Revealed by Numerous Transformation Products Characterized in Key French West Indies Environmental Compartments | Chevallier et al., 2019 | Link |
| The insecticide chlordecone has been used in the French West Indies for decades, resulting in long term pollution, human health problems and social crisis. In addition to bacterial consortia and Citrobacter sp.86 previously described to transform chlordecone into three families of transformation products (A: hydrochlordecones, B: polychloroindenes and C: polychloroindenecarboxylic acids), another bacterium Desulfovibrio sp.86, showing the same abilities has been isolated and its genome was sequenced. Ring-opening dechlorination, leading to A, B and C families, was observed as previously described. Changing operating conditions in the presence of chlordecone gave rise to the formation of an unknown sulfur-containing transformation product instead of the aforementioned ones. Its structural elucidation enabled to conclude to a thiol derivative, which corresponds to an undocumented bacterial reductive sulfidation. Microbial experiments pointed out that the chlordecone thiol derivative was observed in anaerobiosis, and required the presence of an electron acceptor containing sulfur or hydrogen sulfide, in a confined atmosphere. It seems that this new reaction is also active on hydrochlordecones, as the 10-monohydrochlordecone A1 was transformed the same way. Moreover, the chlordecone thiol derivative called F1 was detected in several chlordecone contaminated mangrove bed sediments from Martinique Island, highlighting the environmental relevance of these results. | Transformation of the recalcitrant pesticide chlordecone by Desulfovibrio sp.86 with a switch from ring-opening dechlorination to reductive sulfidation activity | Della-Negra et al., 2020 | Link |
| Chlordecone is a synthetic organochlorine pesticide, extensively used in banana plantations of the French West Indies from 1972 to 1993. Due to its environmental persistence and bioaccumulation, it has dramatic public health and socio-economic impact. Here we describe a method for carbon-directed compound specific isotope analysis (CSIA) for chlordecone and apply it to monitor biotic and abiotic reductive transformation reactions, selected on the basis of their distinct product profiles (polychloroindenes versus lower chlorinated hydrochlordecones). Significant carbon isotopic enrichments were observed for all microbially mediated transformations (?bulk = ?6.8‰ with a Citrobacter strain and ?bulk = ?4.6‰ with a bacterial consortium) and for two abiotic transformations (?bulk = ?4.1‰ with zerovalent iron and ?bulk = ?2.6‰ with sodium sulfide and vitamin B12). The reaction with titanium(III) citrate and vitamin B12, which shows the product profile most similar to that observed in biotic transformation, led to low carbon isotope enrichment (?bulk =?0.8‰). The CSIA protocol was also applied on representative chlordecone formulations previously used in the French West Indies, giving similar chlordecone ?13C values from ?31.1 ± 0.2‰ to ?34.2 ± 0.2‰ for all studied samples. This allows the in situ application of CSIA for the assessment of chlordecone persistence. | Distinct Carbon Isotope Fractionation Signatures during Biotic and Abiotic Reductive Transformation of Chlordecone | Chevallier et al., 2018 | Link |
| Chlordecone is an organochlorine insecticide that has been widely used to control banana weevil in the French West Indies. As a result of this intense use, up to 20,000 ha are contaminated by this insecticide in the French West Indies, and this causes environmental damage and health problems. A scenario of exposure was drawn by French authorities, based on land usage records. Many efforts have been made to monitor the occurrence of chlordecone and its main metabolites using different analytical methods, including GC, GC/MS, LC/MS, and NIRS. Although these different methods allow for the detection and quantification of chlordecone from soils, none of them estimate the bottleneck caused by extraction of this organochlorine from soils with high adsorption ability. In this study, we used 13C10-chlordecone as a tracer to estimate chlordecone extraction yield and to quantify chlordecone in soil extracts based on the 13C/12C isotope dilution. We report the optimization of 13C10-chlordecone extraction from an Andosol. The method was found to be linear from 0.118 to 43 mg kg?1 in the Andosol, with an instrumental detection limit estimated at 8.84 ?g kg?1. This method showed that chlordecone ranged from 35.4 down to 0.18 mg kg?1 in Andosol, Nitisol, Ferralsol, and Fluvisol soil types. Traces of the metabolite ?-monohydrochlordecone were detected in the Andosol, Nitisol, and Ferralsol soil samples. This last result indicates that this method could be useful to monitor the fate of chlordecone in soils of the French West Indies. | Detection and quantification of chlordecone in contaminated soils from the French West Indies by GC-MS using the 13C10-chlordecone stable isotope as a tracer | Martin-Laurent et al., 2013 | Link |
| The historic use of chlordecone (C10Cl10O) as a pesticide to control banana weevil infestations has resulted in pollution of large land areas in the French West Indies. Although currently banned, chlordecone persists because it adsorbs strongly to soil and its complex bis-homocubane structure is stable, particularly under aerobic conditions. Abiotic chemical transformation catalyzed by reduced vitamin B12 has been shown to break down chlordecone by opening the cage structure to produce C9 polychloroindenes. More recently these C9 polychloroindenes were also observed as products of anaerobic microbiological transformation. To investigate the anaerobic biotransformation of chlordecone by microbes native to the French West Indies, microcosms were constructed anaerobically from chlordecone impacted Guadeloupe soil and sludge to mimic natural attenuation and eletron donor-stimulated reductive dechlorination. Original microcosms and transfers were incubated over a period of 8 years, during which they were repeatedly amended with chlordecone and electron donor (ethanol and acetone). Using LC-MS, chlordecone and degradation products were detected in all the biologically active microcosms. Observed products included monohydro-, dihydro- and trihydrochlordecone derivatives (C10Cl10-nO2Hn; n = 1,2,3), as well as “open cage” C9 polychloroindene compounds (C9Cl5-nH3+n n = 0,1,2) and C10 carboxylated polychloroindene derivatives (C10Cl4-nO2H4+n, n = 0–3). Products with as many as 9 chlorine atoms removed were detected. These products were not observed in sterile (poisoned) microcosms. Chlordecone concentrations decreased in active microcosms as concentrations of products increased, indicating that anaerobic dechlorination processes have occurred. The data enabled a crude estimation of partitioning coefficients between soil and water, showing that carboxylated intermediates sorb poorly and as a consequence may be flushed away, while polychlorinated indenes sorb strongly to soil. Microbial community analysis in microcosms revealed enrichment of anaerobic fermenting and acetogenic microbes possibly involved in anaerobic chlordecone biotransformation. It thus should be possible to stimuilate anaerobic dechlorination through donor amendment to contaminated soils, particularly as some metabolites (in particular pentachloroindene) were already detected in field samples as a result of intrinsic processes. Extensive dechlorination in the microcosms, with evidence for up to 9 Cl atoms removed from the parent molecule is game-changing, giving hope to the possibility of using bioremediation to reduce the impact of CLD contamination. | Theoretical approach to chlordecone biodegradation | Macarie et al., 2018 | Link |
